Easy Resistance Calculator
Calculate electrical resistance using Ohm's Law and power formulas. Enter any two known values to find the resistance and other electrical parameters.
Resistance Calculation Formulas
Resistance Calculator – A Complete Friendly Guide
I. Introduction
Resistance plays a vital role in every electrical circuit. It determines how easily electron flow moves through a conductive path and influences voltage, current, and power behavior across components. In simple terms, electrical resistance affects how devices operate, how circuits are designed, and how energy is managed in both alternating current and direct current systems.

A resistance calculator helps users quickly compute values using well-known formulas instead of solving them manually. It assists in circuit planning, component verification, and understanding how different parameters such as resistivity, wire length, and temperature affect total resistance.
II. Basic Concepts of Resistance
Definition and Unit
Resistance is the opposition to electrical current, measured in Ohms (Ω). It influences how voltage, current, and power behave within a circuit, making it a fundamental element of electrical design.
Understanding Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law defines the relationship:
- Voltage (V)
- Current (I, measured in Ampere)
- Resistance (R)
It expresses the idea that:
Higher resistance reduces current, while lower resistance allows more current to flow.
This law applies in interpreting electrical potential, electrical charge, wattage, and conductance. For a deeper dive, check out our Ohm's Law Calculator.
Types of Resistors
A resistance calculator often supports values related to different resistor types, such as:
- SMD resistor, through-hole resistor
- Carbon film, metal film, wirewound resistor
- Variable resistor, potentiometer
- Thermistor and photoresistor

These components vary in tolerance, conductivity, and application.
III. How Resistance Is Calculated
Common Formulas
A calculator typically uses three main formulas:
- Formula R = V / I (from Ohm’s Law)
- Formula R = P / I² (using power and current)
- Formula R = ρ (L / A)
Where ρ = Resistivity, L = Wire length, A = Cross-sectional area
Resistivity and Material Influence
Materials like copper, aluminum, gold, silver, nichrome, tungsten, and constantan all have different resistivity coefficients. Length and area also modify resistance, forming a key part of any conductive path calculation.
Temperature Effects
Temperature affects resistance through the temperature coefficient, which changes values as conductors heat up or cool down. Thermal resistivity and heat dissipation also impact performance.
IV. Types of Resistance Calculations
Series Resistance
A series resistance calculation involves simply adding values — the sum of resistances. Try our Series Resistor Calculator for quick computations.
Parallel Resistance
Parallel resistors require the reciprocal formula, where each resistor’s inverse sum defines total resistance (reciprocal sum). Use our Parallel Resistor Calculator to calculate easily.
Combination Circuits
A resistance network may include both series and parallel parts, requiring Kirchhoff’s Laws, current division, or voltage division to solve the equivalent resistance.
V. Resistor Color Coding
Understanding Color Codes
Physical resistors often use resistor color codes with:
- 4-band resistors
- 5-band resistors
- 6-band resistors
These bands indicate:
- Resistor value
- Multiplier band
- Tolerance band
- Temperature coefficient band
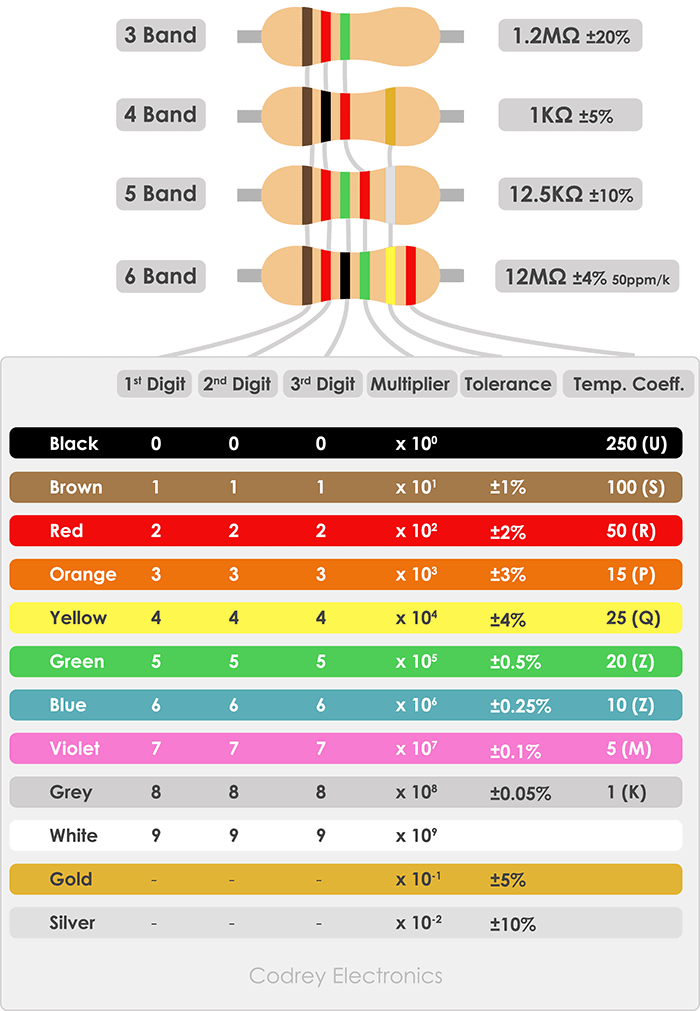
Using Color Bands
A resistance calculator may include options to select color bands and retrieve resistance values based on resistor marking charts, SMD codes, and resistor series such as E12, E24, E48, and E96. Explore our Resistor Color Code Calculator for interactive decoding.
VI. Using a Resistance Calculator
Common Features
Good tools provide:
- Real-time calculation
- Input validation
- Error checking
- Interactive interface
- Band selection tools

Required Inputs
A typical calculator allows:
- Voltage, current, and power input
- Resistivity and wire gauge
- Length and area measurements
- Tolerance percent
- Numeric input with decimal values
- Resistance units (ohms, kiloohms, megaohms)
Types of Calculators
Users may encounter:
- Resistor value calculator
- Total resistance calculator
- Wire resistance calculator
- Batch calculation tools
- Circuit simulation options
These are especially useful in DIY electronics and educational use.
VII. Applications of Resistance Calculators
Resistance calculators assist in:
- Electrical wiring and home circuits
- PCB design and signal conductors
- Industrial circuits
- Electronic repair and prototype testing
- Sensor circuits
- Automation and renewable energy systems
- Engineering education for beginners and students
They simplify decision-making and reduce human error.
VIII. Advanced Topics
Impedance and Reactance
In AC circuits, resistance becomes part of a broader concept known as impedance, influenced by reactance and frequency.
Skin Depth Effects
At high frequencies, conductors exhibit skin depth, where current flows near the surface, impacting effective resistance.
Microfluidic Resistance
Some scientific fields calculate microfluidic resistance, where fluid channels exhibit electrical-like resistance due to their geometry.
Precision Circuits
Engineers sometimes design custom resistance values for specialty circuits, requiring exact resistivity or temperature-coefficient considerations.
IX. Common Mistakes and Tips
Avoid incorrect entries by relying on calculators with input validation.
Always consider tolerance to ensure accuracy.
Check for temperature rise, insulation issues, and resistor power rating to avoid component failure.
X. Conclusion
Accurate resistance calculation is essential for safe and efficient electrical design. A resistance calculator helps users combine theoretical knowledge with practical computation, making circuit work smoother, faster, and more reliable.